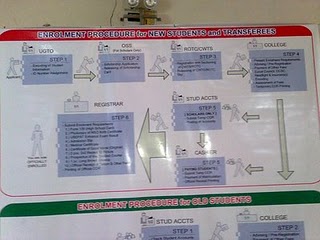
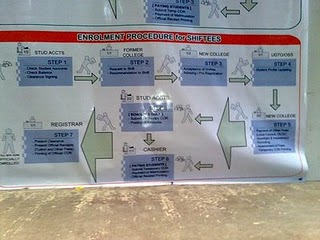
Interview your university network specialist. Ask how various parts of the system communicate with each other throughout the university. (Q) Given the chance to redesign the existing setup, enumerate and discuss your keypoints for an effective and efficient network environment ideal for the university.
We can never deny that technology is growing bigger and had made a big impact in every person’s daily life. On our case, a network is everywhere and a great area for the University to communicate within. In a network, different computer workstations are connected by cabling or wireless systems. This allows them to communicate with each other, including mass electronic mail capabilities. Workstations are sometimes attached to data handling hardware such as servers, which hold a large amount of data, and distribute it as needed to other parts of the network, all of these complex systems require staff to set up, maintain and troubleshoot the entire network to make sure that the business always has the capabilities that the network was intended to support.
Network specialist is the one who is in charge on maintaining and supervising a network. A network specialist is someone who deals with computer networks professionally. The general category of network specialist professionals includes individuals who do a lot of different work with various computer networking systems. They are skilled in various kinds of computer repair and computer maintenance. They are a vital addition to an information technology department, because they can respond quickly to various network issues. When part of a network malfunctions, it can create an extreme problem for a business very quickly.
In the University of Southeastern Philippines, our University Network Specialist is Engr. Ariel Roy L. Reyes, but due to the busy schedule of Engr. Reyes he decided to just cater the student as a class rather than a one on one interview. He was given a questionnaire made by the class and distributed it after. Thus, obviously almost all of us have the same thoughts.
We have asked him how the various parts of the system in the University interact with each other. Unfortunately, he is not the right person to answer this, instead MR. Jappeht M. Fortich and Dr. Tamar Cher R. Mercado, our University Programmers were the best person to share regarding the System Development.
Another question was “What are the components involved in the system(s) in the university? (hardware, software, technology, etc.)”
Engr. Reyes have responded that, “I am not in the right position to discuss the details of the software components used as there are other assigned personnel for such job. However, talking about hardware component and technology used, basically I, assigned as the network administrator, is entrusted to maintain our different servers to run 24/7. Currently, we have our Web Server hosted here in our University in our HP ProLiant ML350 Server. Its an old but stable server set-up here in our Networks Office and has been active since Engr. Val A. Quimno , not yet a dean, was appointed as the Network Administrator. The said server has the following specification:
• Intel Xeon 3.0 GHz, 3.2 GHz, or 3.4 GHz processors (dual processor capability) with 1MB level 2 cache standard. Processors include support for Hyper-Threading and Extended Memory 64 Technology (EM64T)
• Intel® E7520 chipset
• 800-MHz Front Side Bus
• Integrated Dual Channel Ultra320 SCSI Adapter
• Smart Array 641 Controller (standard in Array Models only)
• NC7761 PCI Gigabit NIC (embedded)
• Up to 1 GB of PC2700 DDR SDRAM with Advanced ECC capabilities (Expandable to 8 GB)
• Six expansion slots: one 64-bit/133-MHz PCI-X, two 64-bit/100-MHz PCI-X, one 64-bit/66-MHz PCI-X, one x4 PCI-Express, and one x8 PCI-Express
• New HP Power Regulator for ProLiant delivering server level, policy based power management with industry leading energy efficiency and savings on system power and cooling costs
• Three USB ports: 1 front, 1 internal, 1 rear
• Support for Ultra320 SCSI hard drives (six hot plug or four non-hot plug drives supported standard, model dependent)
• Internalstorage capacity of up to 1.8TB; 2.4TB with optional 2-bay hot plug SCSI drive
• 725W Hot-Plug Power Supply (standard, most models); optional 725W Hot-Pluggable Redundant Power Supply (1+1) available. Non hot plug SCSI models include a 460W non-hot plug power supply.
• Tool-free chassis entry and component access
• Support for ROM based setup utility (RBSU) and redundant ROM
• Systems Insight Manager, SmartStart, and Automatic Server Recovery 2 (ASR-2) included
• Protected by HP Services and a worldwide network of resellers and service providers.
Three-year Next Business Day, on-site limited global warranty. Certain restrictions and exclusions apply. Pre-Failure Notification on processors, memory, and SCSI hard drives.
Aside from it, our mail server running under Compaq Proliant ML330 Server, our oldest server, is also hosted here in our Networks Office. Together with other Servers, such as Proxy and Enrollment Servers, both proxy and our enrollment servers are running in microcomputer/personal computers but with higher specifications to act as servers.
Next question is about the network connectivity, “How do these communicate with one another? (topology, network connectivity, protocols, etc.) – may include data flow/ UML diagrams to better explain.”
According to him, “All Servers are connected in a shared medium grouped as one subnetwork. In general, our network follows the extended star topology which is connected to a DUAL WAN Router that serves as the load balancer between our two Internet Service Providers. All other workstations are grouped into different subnetworks as in star topology branching out from our servers subnetwork as in extended star topology. At present, we are making use of class C IP Address for private IP address assignments. Other workstations IP assignments are configured statically (example: laboratories) while others are Dynamic (example: offices). All workstations are connected via our proxy servers that do some basic filtering/firewall to control user’s access to the internet aside from router filtering/firewall management. So, whenever any workstation has to connect to the internet, it has to pass through software and hardware based firewall.”
He was asked on what are the processes involved in the communication (each system to other systems)?
Relative to what Engr. Reyes mentioned above, all workstations are connected via a proxy server. It means that whenever a workstation is turned on, it requests for an IP address from the proxy server (for dynamically configured IP address) and connect to the network after IP address is acquired. As connection is established, each system can now communicate and share resources within the same subnetwork and to server following the concepts discuss in your Computer Network Class.
About the maintenance of the system, they go along by always checking the network servers. He said “basically, our servers are expected to be in good condition since it is required to be up 24/7. Daily, during my vacant period, monitoring on the servers are observed that includes checking logs, checking hardware performance such as CPU health, etc. If problems are observed, remedies are then and then applied. Once in a week, regular overall checkup is observed as preventive maintenance to ensure not to experience longer downtime if possible.”
In the question if the system follow specific standard, he mentioned that different networking standards was already observed such as cabling standards TIA/EIA 568A-B, different IEEE standards which have been discussed in your Computer Networks Subject, etc. Since he was appointed as the Network Administrator, everything was already in place except for some minor changes.
In terms of the security of the system, the vulnerabilities and risk are being mitigated with some process. They have implemented both software and hardware based filtering/firewall which is a part of a computer system or network that is designed to block unauthorized access while permitting authorized communications. It is a device or set of devices which is configured to permit or deny computer applications based upon a set of rules and other criteria. Essentially, they have considered different mitigation techniques for the risks and vulnerabilities to increase the security in the University network. Aside from these things, constant monitoring on networks activity also increases the security of the system.
With regards to some network interferences and how it affects the business cycle of the University, is somehow unexpected in any network.
Major Interferences are normally encountered as an effect of unforeseen and beyond our control events such as black outs, and the like. The said interference would of course affect University’s day-to-day businesses for obviously this will paralyze all our activities that rely on electricity and further this might cause damage on our network devices, etc. that may later be the reason for longer downtime. Problems encountered by our providers such as connection to the National/International Gateway also affect University’s business such as correlating to University’s Business Partners outside and within the country.
University networking is precisely apparent by most colleges and universities to be one of mainly significant issues they are facing at present. A university grounds network is far more than just a physical infrastructure and planning and building a university grounds network really means mounting an entirely new information setting that will have a profound impact on almost every aspect of campus life. In building networks, campuses are engaged in a change process that is strategically essential to their very nature and existence. For me, before you design your any network setup, you need to understand the physical and logical aspects of your current environment. From a physical standpoint, your design depends on the type and integrity of your network infrastructure.
However, your hardware and software environment affects the details of how users adopt the system. So it is important to understand that network planning really means planning a whole new environment that will encompass information, communication, and entertainment on the campus. The network will provide a powerful, dynamic, new channel of access to the world of information. It will also enhance and fundamentally alter the communication mechanisms on campus. And whether we want it or not, the network will provide a wide range of new entertainment opportunities. This new environment will encompass or touch all the information technology area which will challenge, compete with, and sometimes replace existing modes of campus communications, information access, administrative work, power hierarchies, and budgeting systems.
Reference:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_network